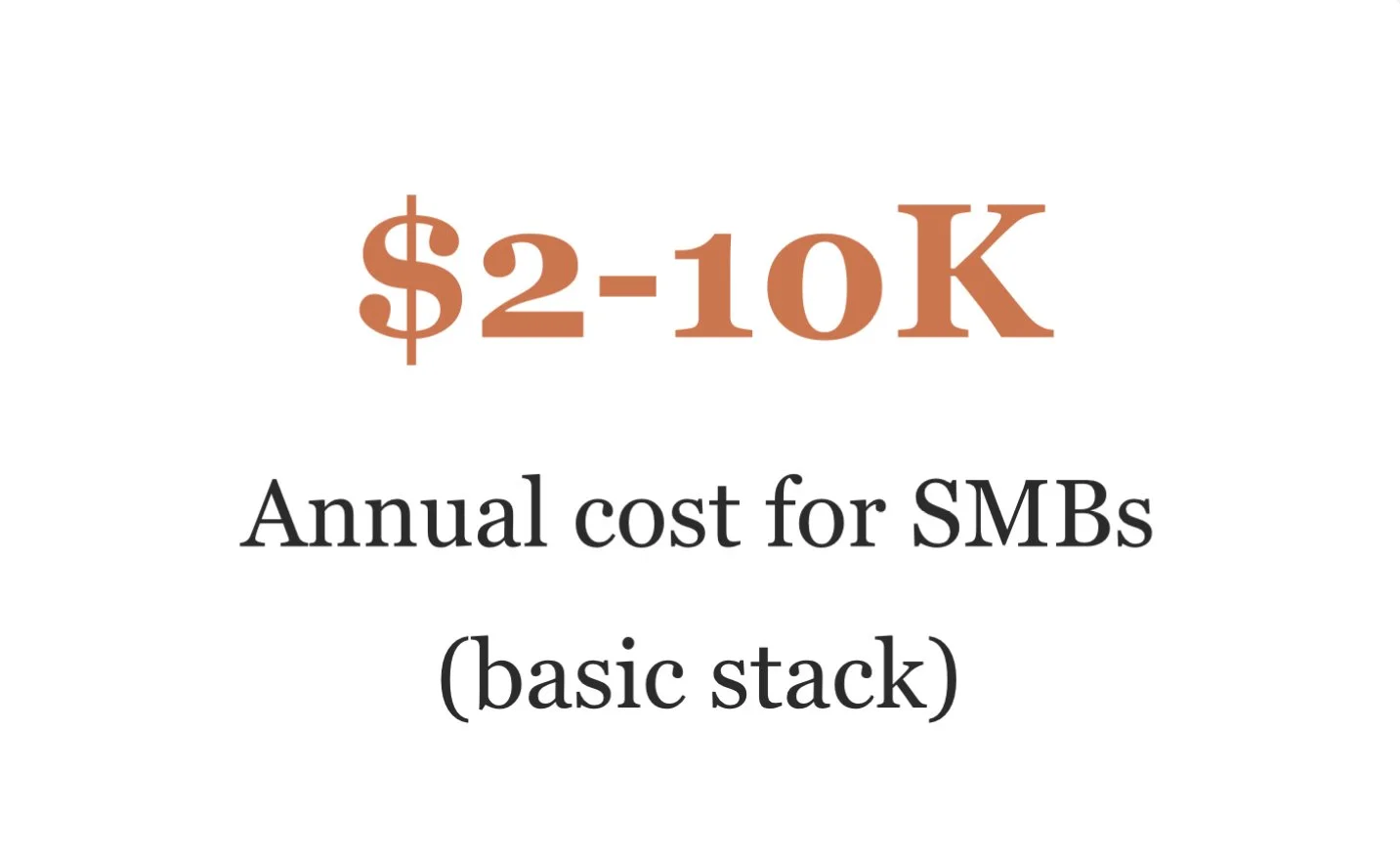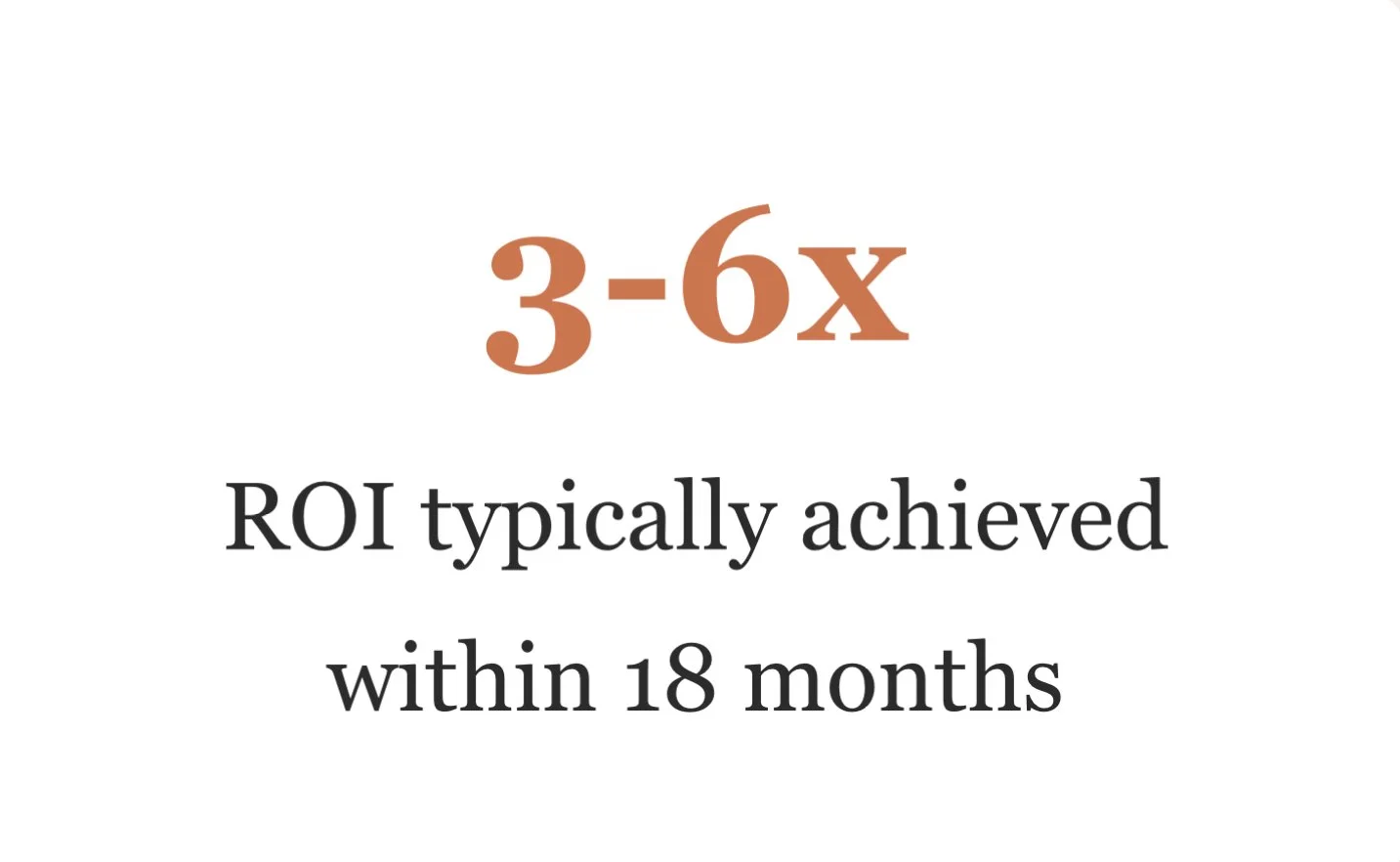The Fear-Feedback Disconnect
Why Businesses Worldwide Avoid the Customer Conversations That Drive Success
Executive Summary
Despite overwhelming evidence that customer feedback drives business success, a critical disconnect exists: businesses worldwide systematically avoid the very conversations that could transform their competitive position. Our comprehensive analysis of global consumer behavior reveals that only 1 in 26 unhappy customers actually voice their concerns, while 94% of consumers avoid businesses with negative reviews. Yet businesses remain reluctant to proactively seek feedback, trapped by fears of negative responses and lacking systematic approaches to customer input collection.
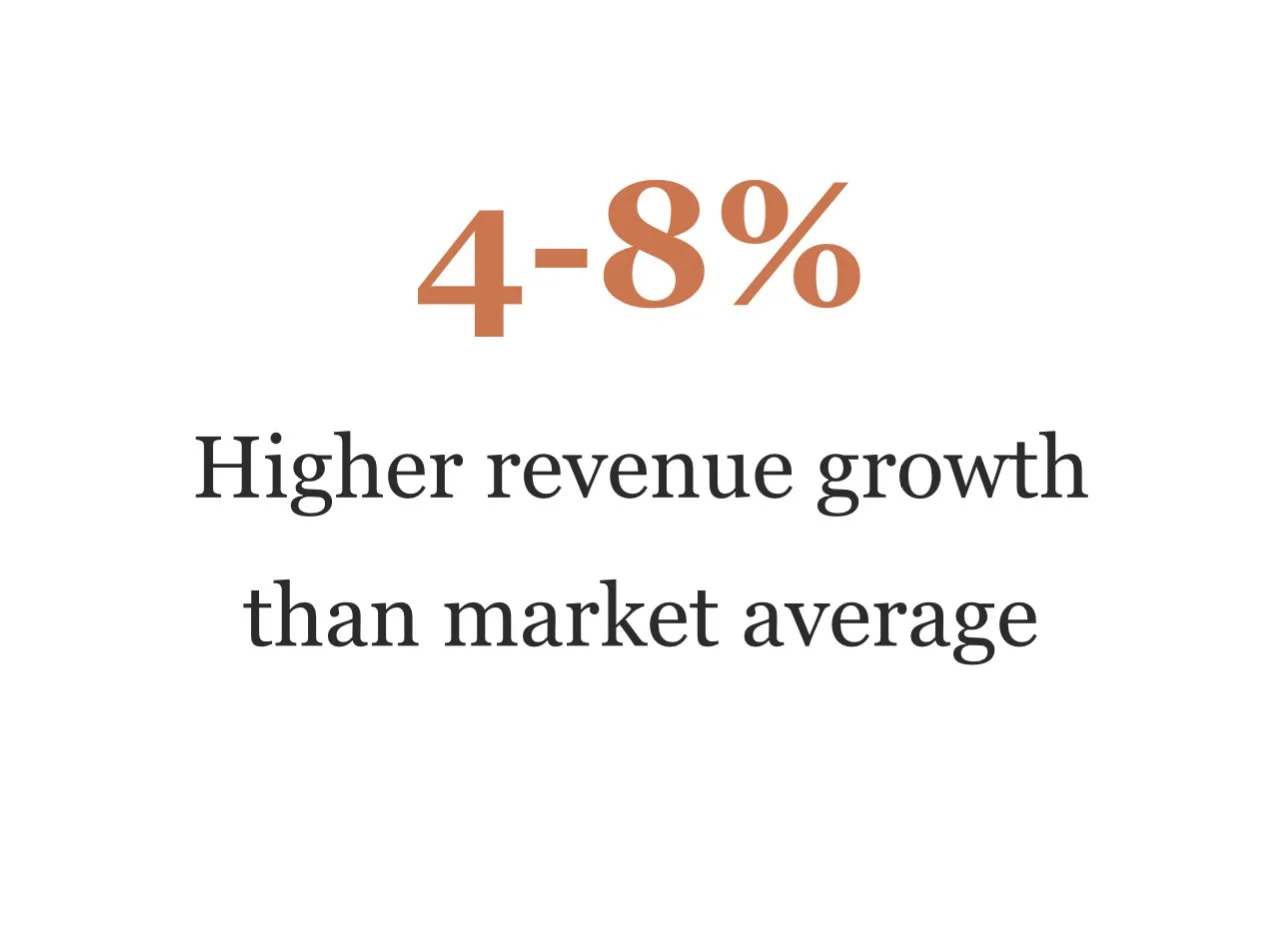
This research presents the Fear-to-Feedback Framework (F2F), a five-component strategic model that addresses the psychological, operational, and structural barriers preventing businesses from harnessing customer feedback as a competitive advantage. Our findings demonstrate that companies implementing systematic feedback collection see 4-8% higher revenue growth than competitors, while those avoiding feedback risk silent customer exodus and missed innovation opportunities.
The Silent Exodus: Understanding the Customer Feedback Crisis
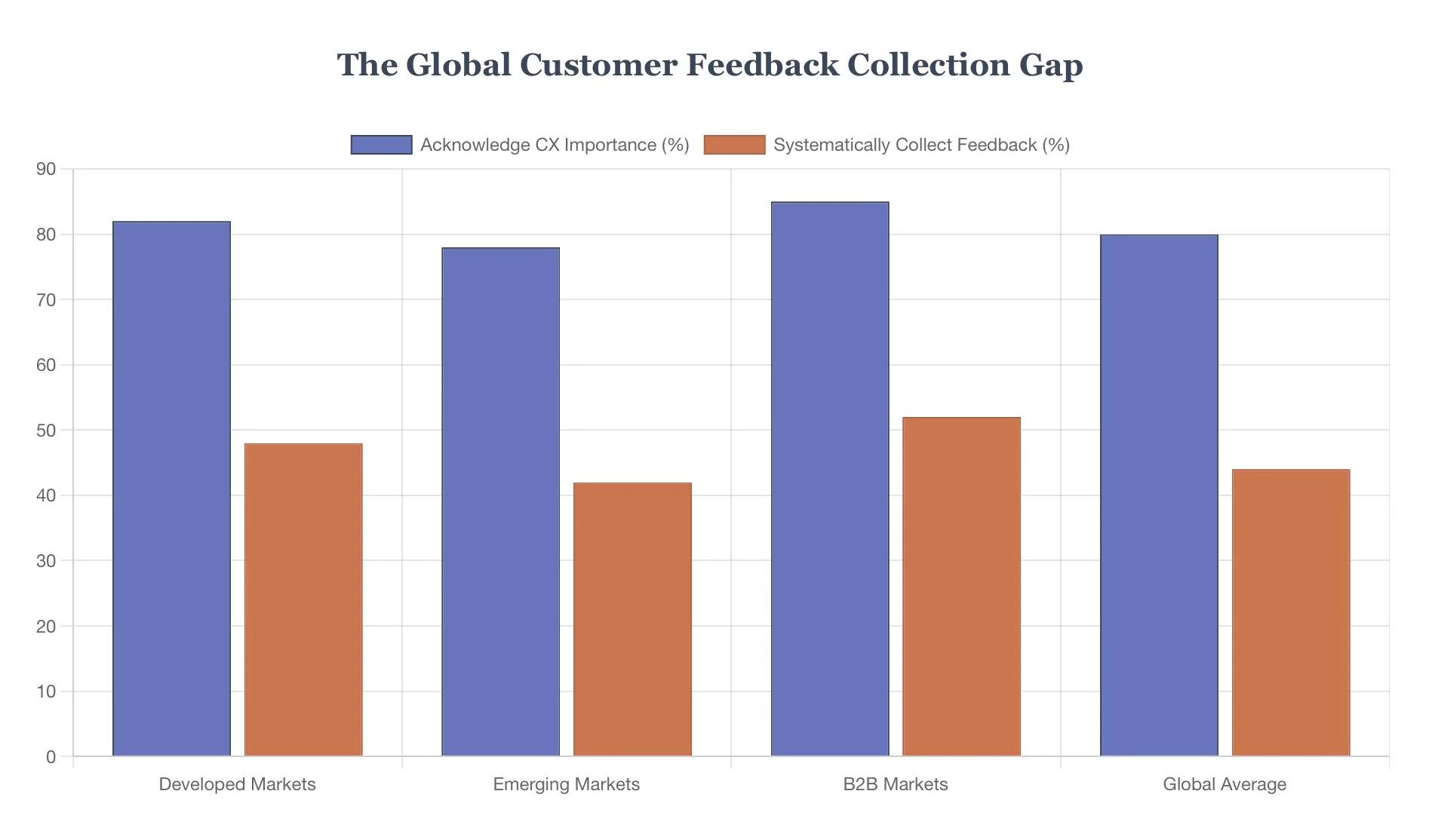
In today's hyperconnected marketplace, customer feedback has evolved from a nice-to-have insight into a mission-critical business function. Yet a profound contradiction exists between the acknowledged importance of customer input and businesses' willingness to actively seek it. Recent research across global markets reveals a concerning pattern: while 80% of companies recognize customer experience as a key differentiator, fewer than half systematically collect and act upon customer feedback.
This disconnect becomes more alarming when examined through the lens of customer behavior. Our analysis of global consumer sentiment data reveals that only 1 in 26 unhappy customers actually voice their complaints, yet 13% of dissatisfied customers will share their negative experience with 15 or more people. The mathematical implications are sobering: for every complaint received, businesses likely have 25 additional dissatisfied customers spreading negative word-of-mouth without the business's knowledge.
The Fear-to-Feedback Framework: Five Barriers to Customer Input
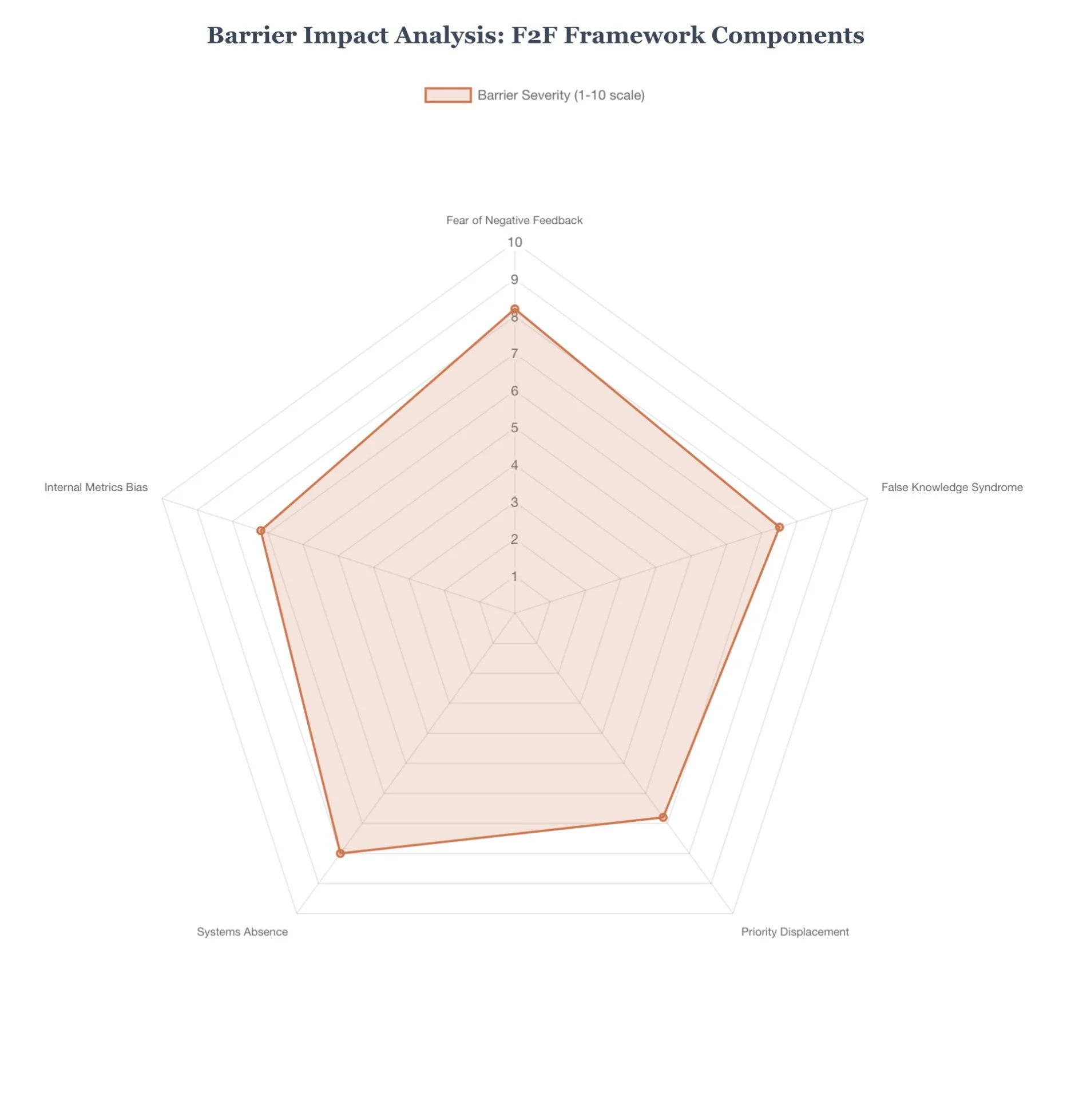
Through extensive research combining behavioral psychology, business performance data, and cross-market consumer studies, we've identified five fundamental barriers that prevent businesses from effectively collecting customer feedback. These barriers form what we term the "Fear-to-Feedback" (F2F) Framework:
The F2F Framework Components
1. Fear of Negative Feedback (Psychological Barrier)
Manifestation: Businesses avoid feedback collection due to anxiety about criticism and potential damage to team morale or leadership authority.
Research Finding: 79% of consumers who complained online about poor customer experience were ignored, suggesting widespread avoidance behaviors.
Business Impact: Creates a false sense of security while allowing problems to compound silently.
2. False Knowledge Syndrome (Cognitive Barrier)
Manifestation: Senior leadership believes they already understand customer needs, particularly in established companies where leaders become isolated from frontline interactions.
Research Finding: 80% of businesses believe they deliver superior customer experiences, but only 8% of customers agree.
Business Impact: Prevents recognition of evolving customer needs and emerging dissatisfaction areas.
3. Priority Displacement (Operational Barrier)
Manifestation: During scaling periods, external growth takes precedence over internal feedback mechanisms, causing customer input collection to fall down priority lists.
Research Finding: Only 44% of organizations plan to increase CX investment, despite 81% viewing customer experience as a growing priority.
Business Impact: Creates disconnect between stated priorities and resource allocation.
4. Systems Absence (Structural Barrier)
Manifestation: Lack of defined processes for feedback collection, analysis, and action creates overwhelming complexity that discourages systematic approaches.
Research Finding: 54% of organizations cite fragmented or siloed data as their biggest barrier to leveraging customer insights.
Business Impact: Feedback collection becomes ad-hoc and ineffective, reinforcing avoidance behaviors.
5. Internal Metrics Bias (Strategic Barrier)
Manifestation: Over-reliance on internal performance indicators while undervaluing external customer perspectives creates strategic blind spots.
Research Finding: 58% of agents report that lack of customer data causes negative experiences, yet many businesses prioritize internal metrics over customer input.
Business Impact: Decisions based on incomplete information lead to customer-business misalignment.
The Cost of Feedback Avoidance
The financial implications of feedback avoidance extend far beyond missed improvement opportunities. Our analysis reveals a cascade of negative business impacts that compound over time:
"It takes roughly 40 positive customer experiences to undo the damage of a single negative review. The mathematics of reputation management heavily favor proactive feedback collection over reactive damage control."
Silent Customer Exodus
Perhaps the most insidious cost of feedback avoidance is what we term "silent customer exodus" – the departure of dissatisfied customers without warning signals. Research indicates:
91% of unhappy customers leave without complaining, providing no opportunity for recovery
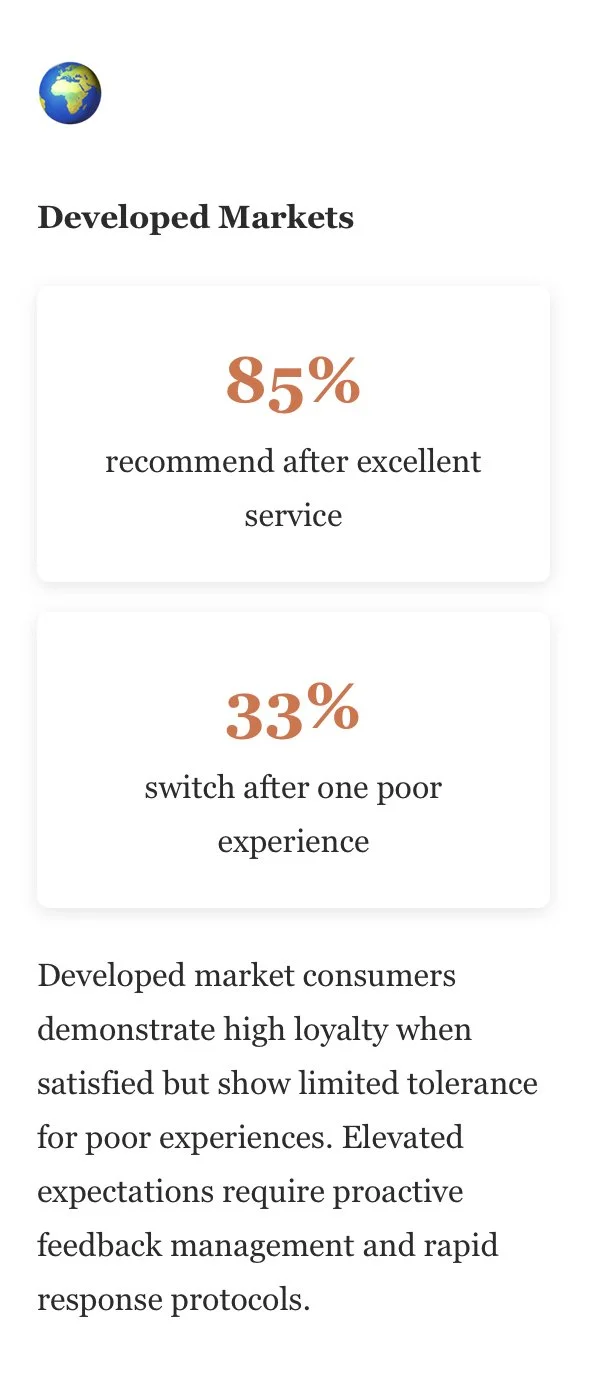
59% of customers abandon brands after a single poor experience, making proactive monitoring critical
It takes 12 positive experiences to overcome one unresolved negative experience, highlighting the asymmetric nature of customer sentiment
Competitive Disadvantage Accumulation
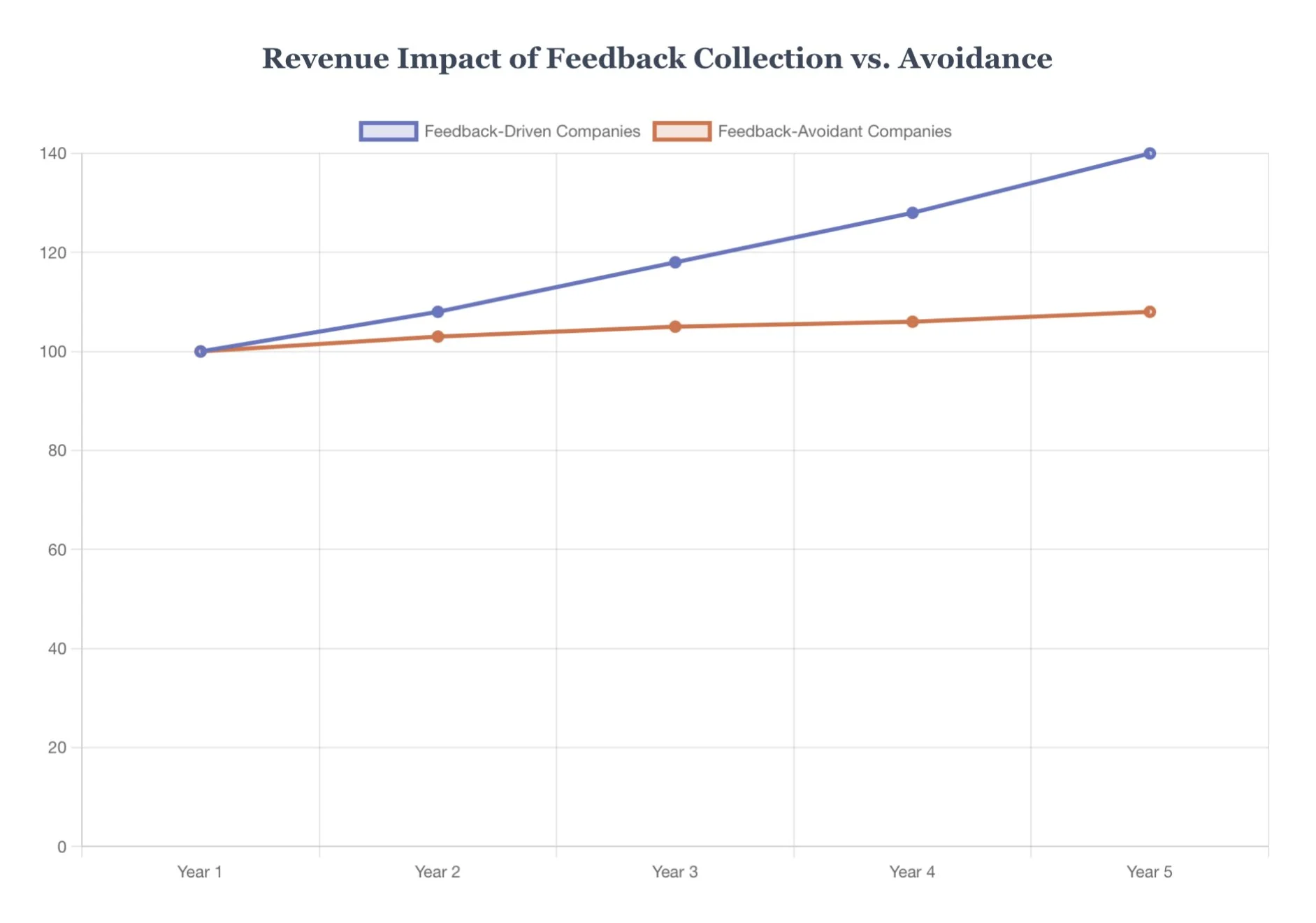
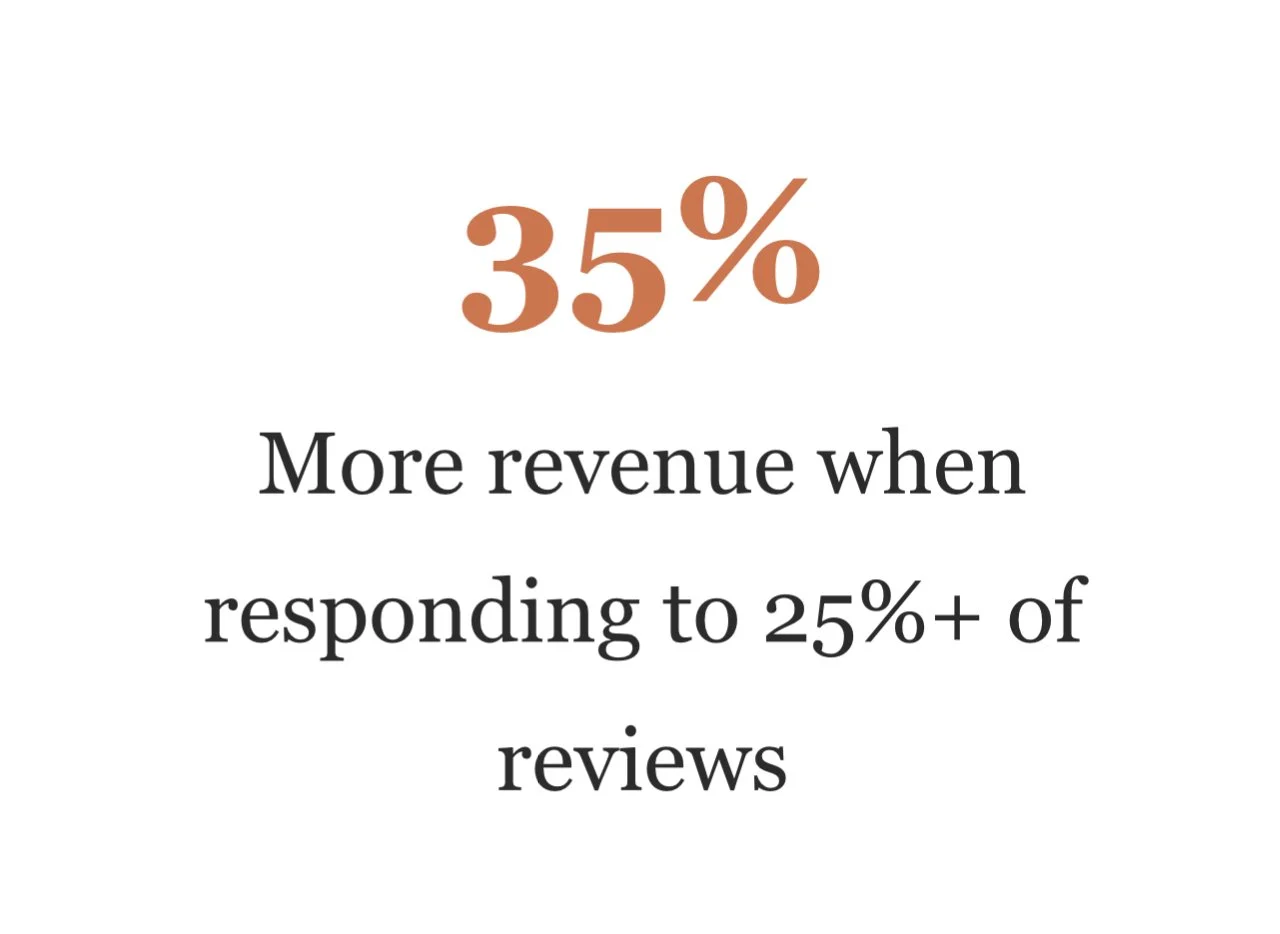
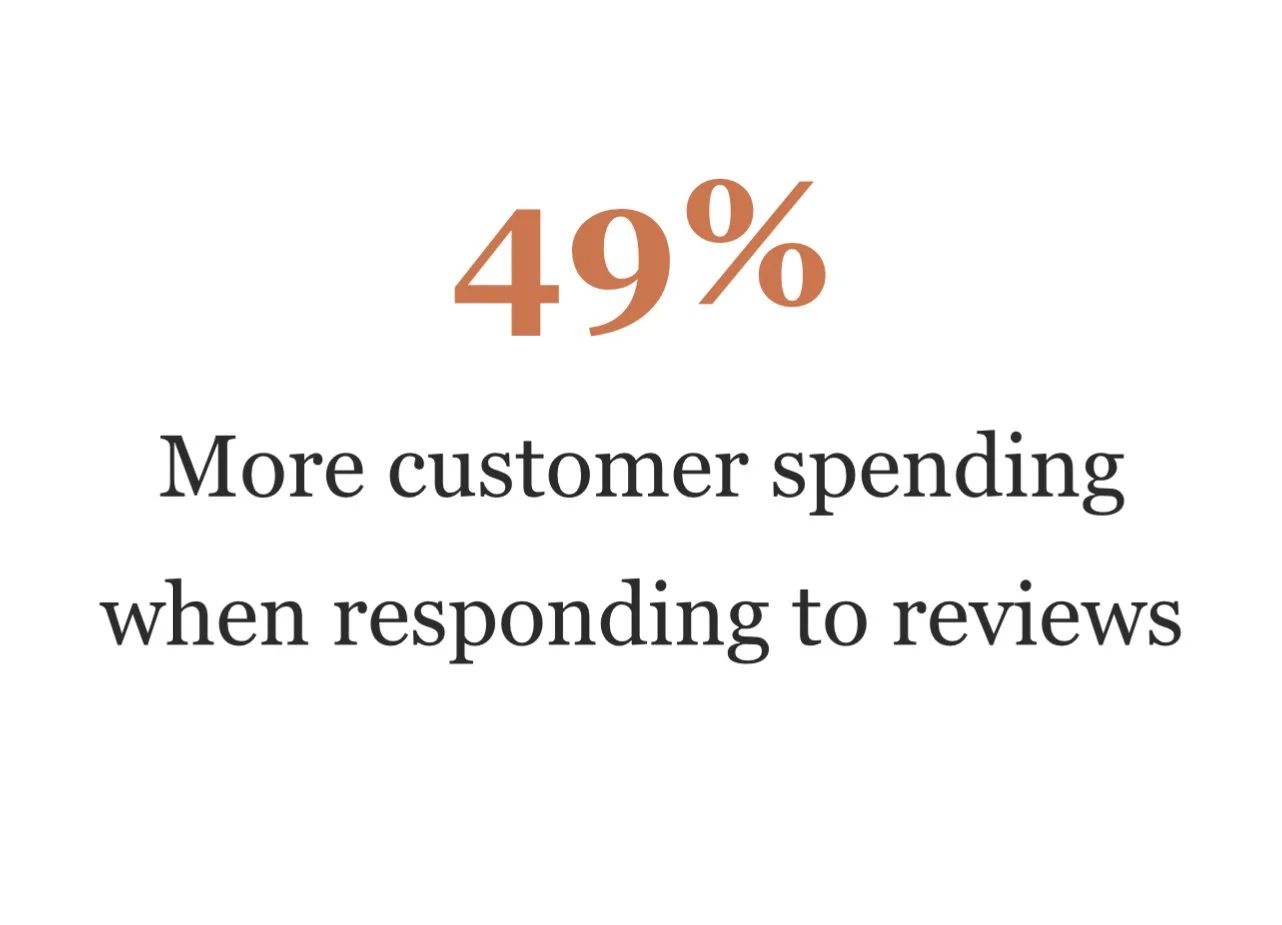
Businesses avoiding feedback collection systematically disadvantage themselves against competitors who embrace customer input. Companies that actively collect and respond to feedback demonstrate:
Strategic Solutions: Overcoming the F2F Barriers
Successfully transitioning from feedback avoidance to feedback advantage requires systematic approaches that address each F2F Framework component. Our research identifies specific interventions that have proven effective across US, UK, and Australian markets:
1. Reframing Negative Feedback as Strategic Intelligence
The most successful organizations reframe negative feedback from threat to opportunity. This cognitive shift requires:
Leadership Modeling: Senior executives publicly discussing learnings from critical feedback
Metrics Rebalancing: Tracking "feedback velocity" alongside traditional performance indicators
Response Training: Equipping teams with skills to handle difficult conversations constructively
2. Implementing Specific Feedback Protocols
Moving beyond broad, overwhelming questions to targeted, actionable inquiries increases both response rates and insight quality:
The Start-Stop-Keep Framework
Start: "What should we begin doing to improve your experience?"
Stop: "What should we stop doing that creates friction or frustration?"
Keep: "What are we doing well that you want us to continue?"
This framework, adapted from Jim Collins' "Good to Great" methodology, provides structured insight while reducing respondent overwhelm.
3. Building Anonymous Feedback Channels
Research consistently shows that anonymity increases feedback candor and volume. Successful implementations include:
Anonymous survey platforms with mobile optimization
Third-party feedback collection to reduce bias concerns
Clear data use policies that build trust in anonymity promises
Feedback Response Rates: Anonymous vs. Identified Collection
Implementation Roadmap: Three-Phase Transformation
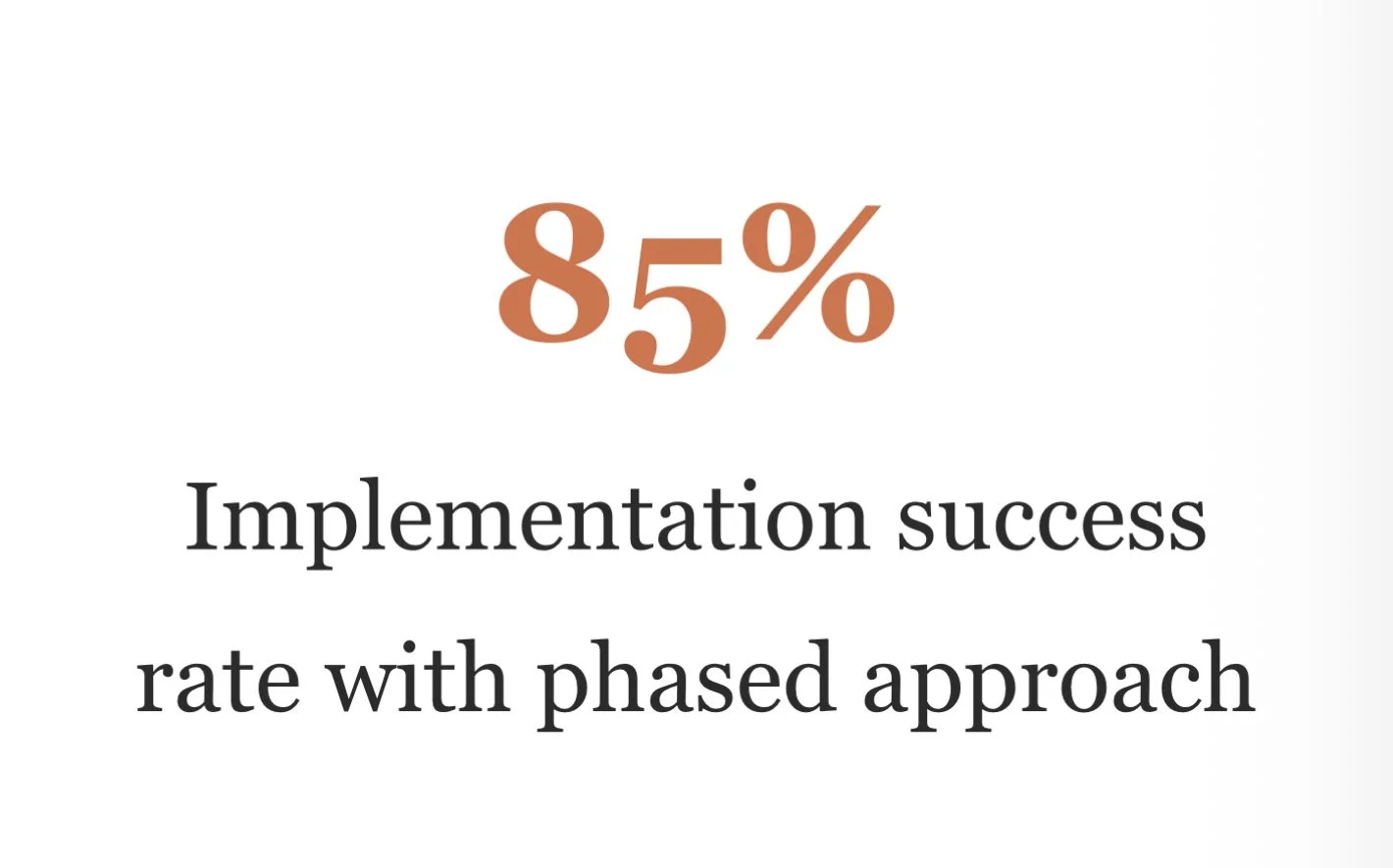
Successfully implementing systematic feedback collection requires a phased approach that builds organizational capability while demonstrating early wins. Our recommended roadmap spans 12-18 months across three distinct phases:
Technology Stack Recommendations
Successful feedback collection requires appropriate technological infrastructure. Based on market analysis and implementation success rates, we recommend a tiered approach:
Cultural Transformation: From Fear to Feedback-Driven Growth
The most successful feedback transformations involve fundamental cultural shifts that permeate organizational thinking and decision-making. This requires addressing both individual psychological barriers and systemic organizational patterns.
Leadership Modeling and Vulnerability
Research consistently demonstrates that leadership behavior patterns cascade throughout organizations. When executives model feedback-seeking behavior and demonstrate constructive responses to criticism, it creates psychological safety for feedback throughout the organization.
"Remember the Human Element: As 'Scaling Up' astutely points out, 'we're all in the same business: people to people'. Treat feedback conversations as genuine dialogues aimed at understanding another person's experience, rather than a purely transactional data-gathering exercise."
Systematic Feedback Integration
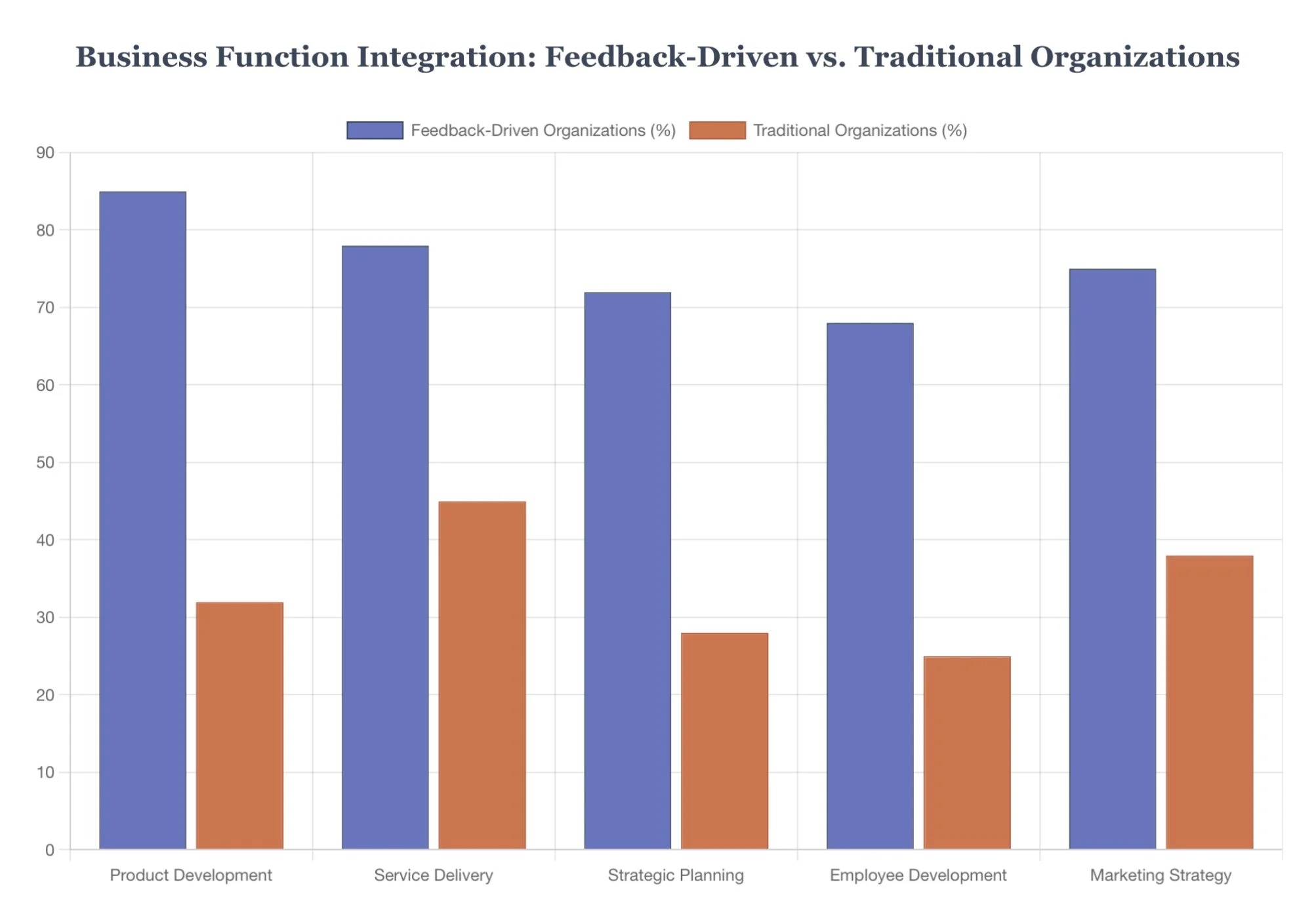
Organizations achieving sustained feedback advantage integrate customer input into multiple business functions:
Product Development: Customer feedback drives feature prioritization and design decisions
Service Delivery: Feedback loops identify and resolve operational friction points
Strategic Planning: Customer insights inform market positioning and competitive strategy
Employee Development: Customer feedback enhances training and performance management
Measuring Success: Key Performance Indicators for Feedback Systems
Effective feedback programs require systematic measurement approaches that track both operational efficiency and business impact. Our research identifies critical metrics across three dimensions:
Collection Metrics
Response Rate: Percentage of feedback requests resulting in responses (target: 25-40%)
Channel Diversity: Number of feedback collection touchpoints (minimum: 3-5)
Feedback Velocity: Time between customer experience and feedback receipt (target: <24 hours)
Processing Metrics
Response Time: Time between feedback receipt and initial response (target: <24 hours)
Resolution Rate: Percentage of actionable feedback resulting in changes (target: 70%+)
Sentiment Trends: Directional movement in customer sentiment over time
Business Impact Metrics
Customer Retention: Impact of feedback implementation on churn rates
Revenue Growth: Correlation between feedback activity and financial performance
Referral Rates: Changes in customer advocacy and word-of-mouth marketing
Universal Implementation Considerations
While the F2F Framework applies across markets, successful implementation requires adaptation to regional business cultures and consumer expectations:
Future Trends and Emerging Opportunities
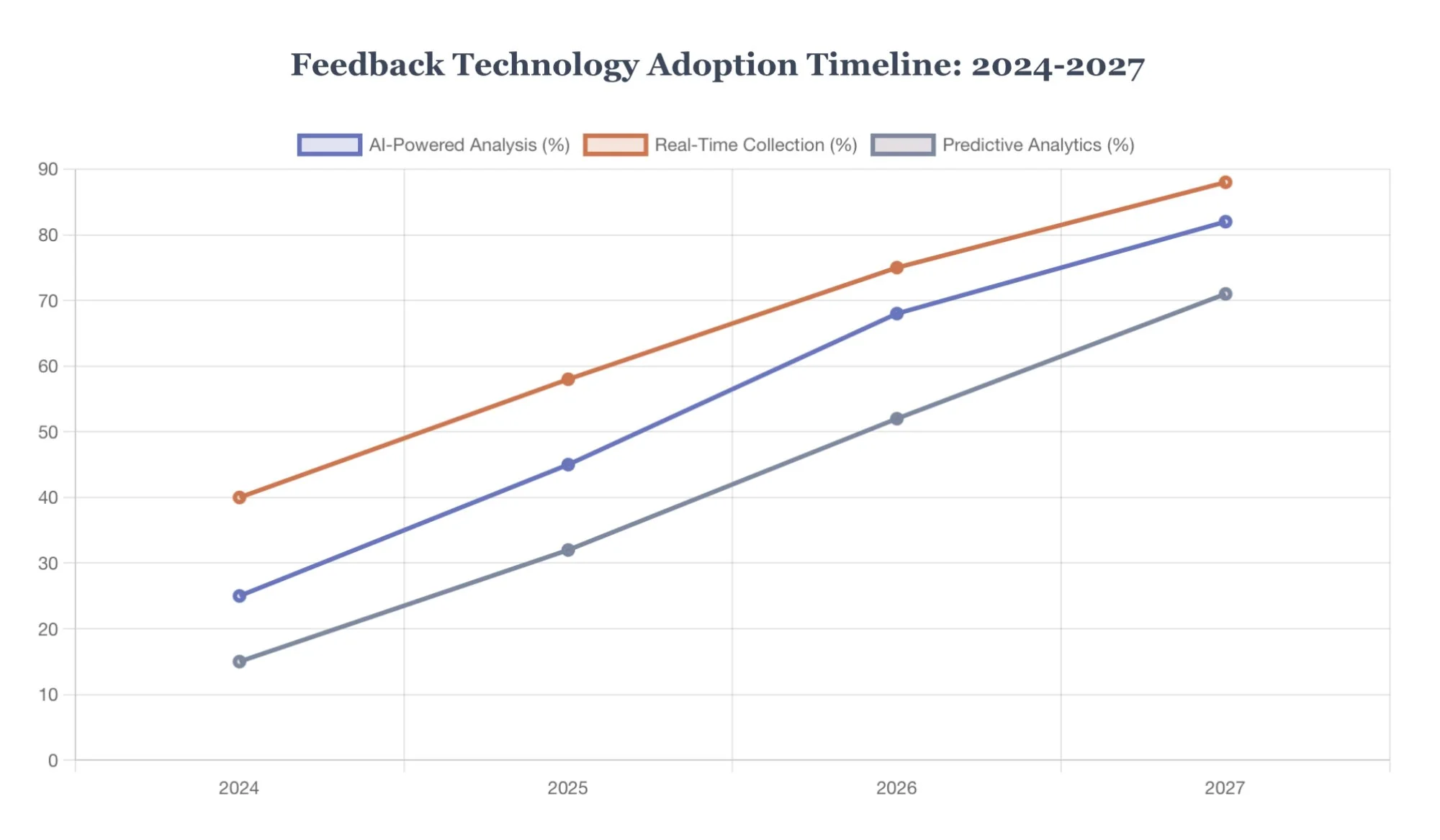
The customer feedback landscape continues evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancement and changing consumer expectations. Organizations implementing feedback systems today must consider emerging trends:
AI-Powered Feedback Analysis
By 2025, 75% of organizations will abandon traditional NPS measurement in favor of AI-driven sentiment analysis that provides real-time insights and predictive modeling capabilities.
Proactive Feedback Collection
Gartner predicts that proactive customer service interactions will outnumber reactive ones by 2025, requiring businesses to anticipate feedback needs rather than waiting for customer-initiated contact.
Omnichannel Integration
Successful feedback programs will seamlessly integrate across all customer touchpoints, creating unified customer experience profiles that inform personalized service delivery.
From Fear to Competitive Advantage
The customer feedback challenge represents both the greatest obstacle and the most significant opportunity facing modern businesses. While the natural human tendency toward feedback avoidance creates psychological and operational barriers, the businesses that overcome these challenges gain disproportionate competitive advantages.
Our research demonstrates that systematic feedback collection, when implemented through the Fear-to-Feedback Framework, transforms customer relationships from transactional interactions into strategic partnerships. The mathematics are compelling: businesses that proactively collect and act upon customer feedback achieve 4-8% higher revenue growth, experience improved customer retention, and develop innovation capabilities that distance them from competitors.
The path forward requires courage—the courage to hear difficult truths, to acknowledge imperfections, and to engage in genuine dialogue with customers. But for organizations willing to make this journey, customer feedback becomes not just a business tool, but a strategic weapon in an increasingly competitive marketplace.
The question facing business leaders is not whether to collect customer feedback, but whether to lead or follow in the feedback-driven transformation of modern commerce.